
Version Show the Docker version information Update Update configuration of one or more containers Unpause Unpause all processes within a container Top Display the running processes of a container Stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics Start Start one or more stopped containers Save Save one or more images to a tar archive Push Push an image or a repository to a registry Pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry Port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the CONTAINER Pause Pause all processes within a container Load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN Inspect Return low-level information on a container or image Import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
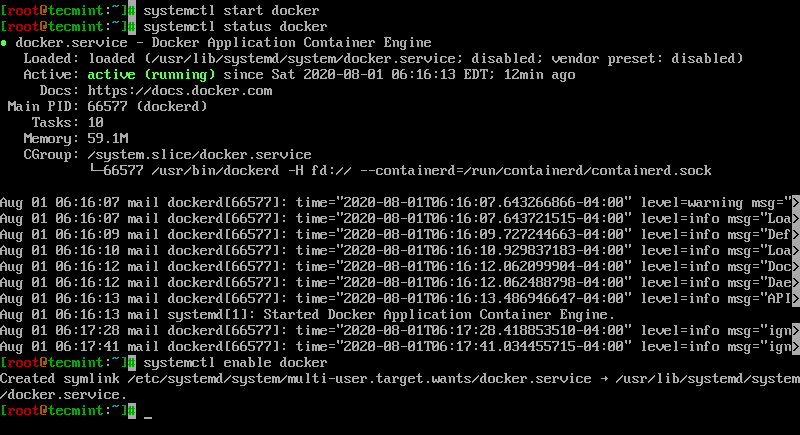

Is the docker daemon running on this host?. Outputdocker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon. The output should be similar to the following, showing that the service is active and running: It will add the official Docker repository, download the latest version of Docker, and install it:Īfter installation has completed, start the Docker daemon: This section shows you how to do just that.īut first, let’s update the package database: To get the latest and greatest version, install Docker from the official Docker repository.
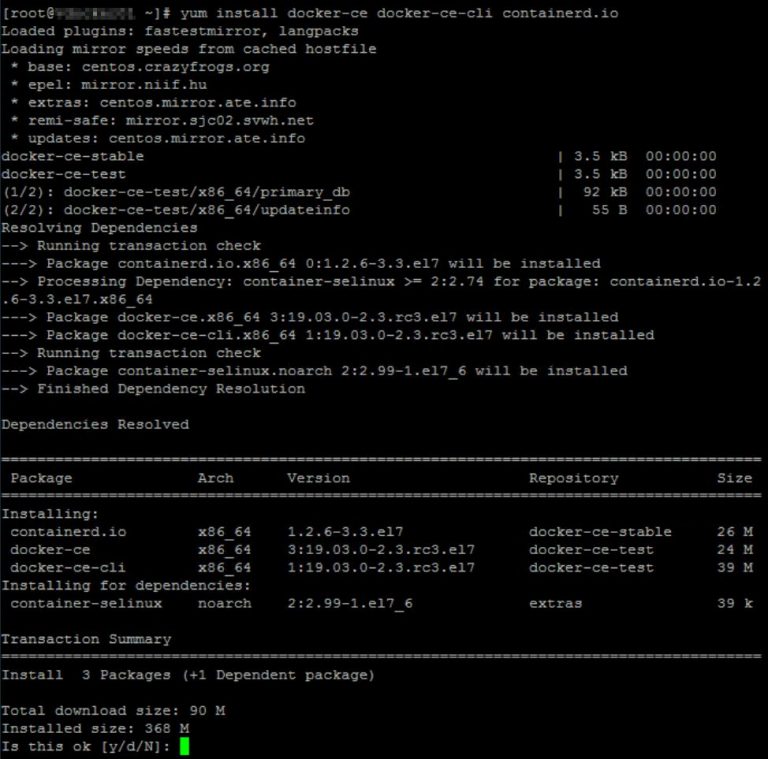
The Docker installation package available in the official CentOS 7 repository may not be the latest version. Initial Setup Guide for CentOS 7 explains how to add users and give them sudo access. If root access is required for the command, it will be preceded by sudo. The default 64-bit CentOS 7 Droplet meets these requirements.Īll the commands in this tutorial should be run as a non-root user. Note: Docker requires a 64-bit version of CentOS 7 as well as a kernel version equal to or greater than 3.10.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
